使用自定義參數(shù)方式實現(xiàn) superset 實現(xiàn)SQL動態(tài)查詢
1����、啟用參數(shù):config.py 設(shè)置"ENABLE_TEMPLATE_PROCESSING": True
2�����、當前superset v1.2版本支持的參數(shù)包括:
{{ current_username() }} 當前登錄用戶名
{{ current_username(add_to_cache_keys=False) }} 不從緩存中獲取登錄用戶名�,默認從緩存獲取
{{ current_user_id()}} 當前登錄用戶ID
{{ current_user_id(add_to_cache_keys=False) }} 不從緩存中獲取登錄用戶ID,默認從緩存獲取
{{ url_param('custom_variable') }} url 參數(shù)�����,比如127.0.0.1:8001\dashboard?abc=123�����,參數(shù)就是{{ url_param('abc') }} 結(jié)果就是123
{{ cache_key_wrapper() }} 還沒有弄明白啥用
{{ filter_values("字段名") }} 獲取dashboard filter_box組件對某個字段的篩選結(jié)果
{{ from_dttm }} 獲取dashboard filter_box組件日期篩選的開始時間
{{ to_dttm }} 獲取dashboard filter_box組件日期篩選的結(jié)束時間
{{ get_filters() }} 暫時沒有弄明白
除此之外,還可以自定義參數(shù)���,自定義參數(shù)方法:
①修改superset/jinja_context.py文件��,修改三個地方:
regex = re.compile(
r"\{\{.*("
r"current_user_id\(.*\)|"
r"current_username\(.*\)|"
r"current_userroles\(.*\)|"
r"isadmin\(.*\)|"
r"cache_key_wrapper\(.*\)|"
r"url_param\(.*\)"
r").*\}\}"
)
↑↑↑↑注意此處的 current_userroles 和 isadmin 是我自定義的���,源文件沒有
def current_user_id(self, add_to_cache_keys: bool = True) -> Optional[int]:
"""
Return the user ID of the user who is currently logged in.
:param add_to_cache_keys: Whether the value should be included in the cache key
:returns: The user ID
"""
if hasattr(g, "user") and g.user:
if add_to_cache_keys:
self.cache_key_wrapper(g.user.get_id())
return g.user.get_id()
return None
def current_username(self, add_to_cache_keys: bool = True) -> Optional[str]:
"""
Return the username of the user who is currently logged in.
:param add_to_cache_keys: Whether the value should be included in the cache key
:returns: The username
"""
if g.user and hasattr(g.user, "username"):
if add_to_cache_keys:
self.cache_key_wrapper(g.user.username)
return g.user.username
return None
def current_userroles(self, add_to_cache_keys: bool = True) -> Optional[str]:
"""
Return the roles of the user who is currently logged in.
:param add_to_cache_keys: Whether the value should be included in the cache key
:returns: The userroles
"""
if g.user and hasattr(g.user, "roles"):
if add_to_cache_keys:
user_roles = "/".join([role.name.lower() for role in list(g.user.roles)])
self.cache_key_wrapper(user_roles)
print(user_roles)
return user_roles
"""admin in user_roles"""
return None
def isadmin(self, add_to_cache_keys: bool = True) -> Optional[str]:
"""
Return the roles of the user who is currently logged in.
:param add_to_cache_keys: Whether the value should be included in the cache key
:returns: The userroles
"""
if g.user and hasattr(g.user, "roles"):
if add_to_cache_keys:
user_roles = [role.name.lower() for role in list(g.user.roles)]
return "admin" in user_roles
return None
↑↑↑↑仿照系統(tǒng)自帶的 current_username 編造自己的函數(shù),我寫了current_userroles 和 isadmin
class JinjaTemplateProcessor(BaseTemplateProcessor):
def set_context(self, **kwargs: Any) -> None:
super().set_context(**kwargs)
extra_cache = ExtraCache(self._extra_cache_keys)
self._context.update(
{
"url_param": partial(safe_proxy, extra_cache.url_param),
"current_user_id": partial(safe_proxy, extra_cache.current_user_id),
"current_username": partial(safe_proxy, extra_cache.current_username),
"current_userroles": partial(safe_proxy, extra_cache.current_userroles),
"isadmin": partial(safe_proxy, extra_cache.isadmin),
"cache_key_wrapper": partial(safe_proxy, extra_cache.cache_key_wrapper),
"filter_values": partial(safe_proxy, filter_values),
}
)
↑↑↑↑仿照系統(tǒng)自帶的 current_username 編造自己的函數(shù)����,我寫了current_userroles 和 isadmin
就是這3個地方�,但是注意,自己在第二步早的函數(shù)���,返回值必須是:
ALLOWED_TYPES = (
NONE_TYPE,
"bool",
"str",
"unicode",
"int",
"long",
"float",
"list",
"dict",
"tuple",
"set",
)
否則會提示錯誤,或者自己修改這個types��,我是轉(zhuǎn)換,比如上面那個g.user.roles 返回的結(jié)果就不是上面類型,導(dǎo)致我一直不成功�,最后修改了下,才可以
3�����、判斷是否自定義成功:
在superset sql lab中執(zhí)行如下代碼,如果能被解析,就說明成功
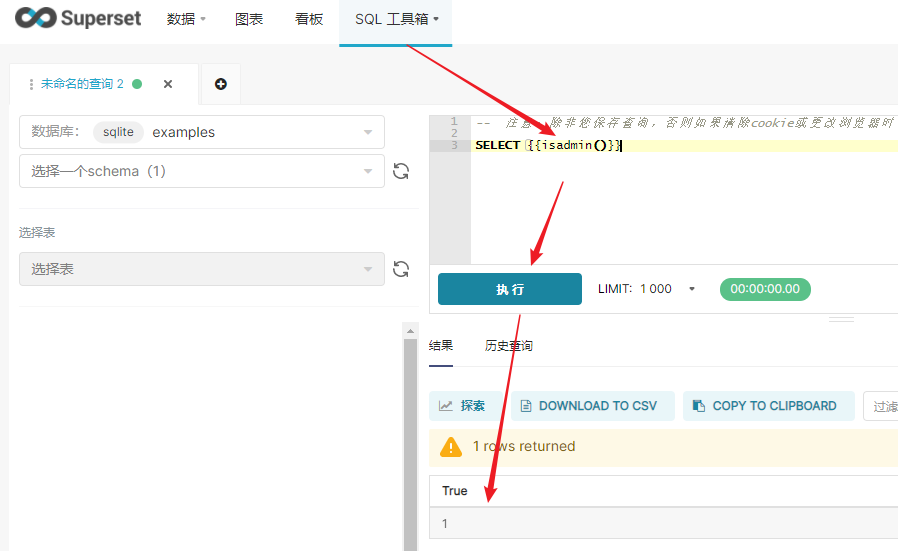
4�����、應(yīng)用案例:

在dataset里面����,動態(tài)訪問數(shù)據(jù)源,數(shù)據(jù)源添加where語句:select * from sales where salesname =' {{current_username()}}'
dashboard里面�����,通過獲取篩選器的結(jié)果�,然后獲取其他表應(yīng)當顯示的數(shù)據(jù)范圍:
select DATE,risktype,sum(num) as num from
(SELECT date , customerid,product,risktype ,count(*) as num
from v_superset_forecast_risk group by date , customerid,product,risktype ) a
join
(select distinct customer_code,product from v_superset_access
where name='{{ current_username() }}' )access
on a.customerid=access.customer_code
and a.product=access.product
and DATE_FORMAT(date,'%Y-%m')> DATE_FORMAT(date_sub(STR_TO_DATE(concat( {{ "'" + "', '".join(filter_values('yearmonthend')) + "'" }},'-01'), '%Y-%m-%d'), interval 12 month),'%Y-%m')
and DATE_FORMAT(date,'%Y-%m')={{ "'" + "', '".join(filter_values('yearmonthend')) + "'" }}
group by DATE,risktype
因為sql里面可以使用jinja 表達式,比如判斷篩選當前沒有篩選的時候��,獲取什么數(shù)據(jù)
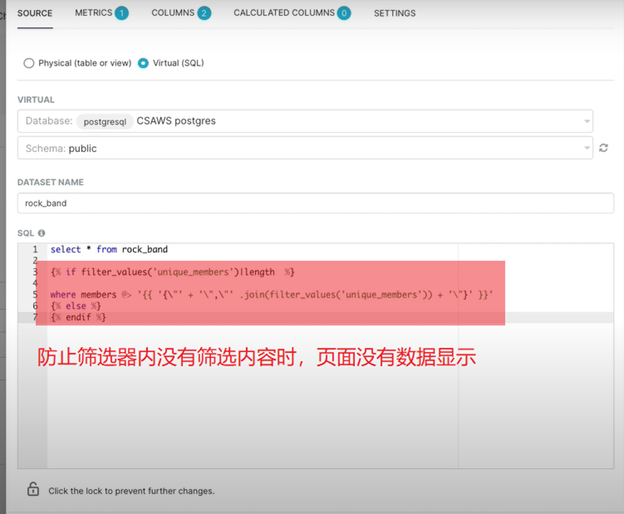
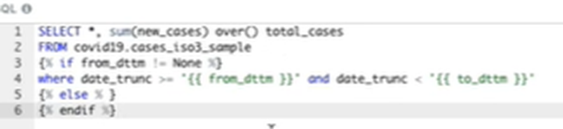
注意{% %} 內(nèi)部使用參數(shù)的時候��,不需要加{{}}����,否則報錯
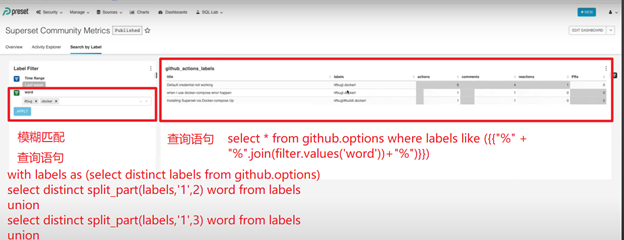
通過篩選器實現(xiàn)模糊查詢
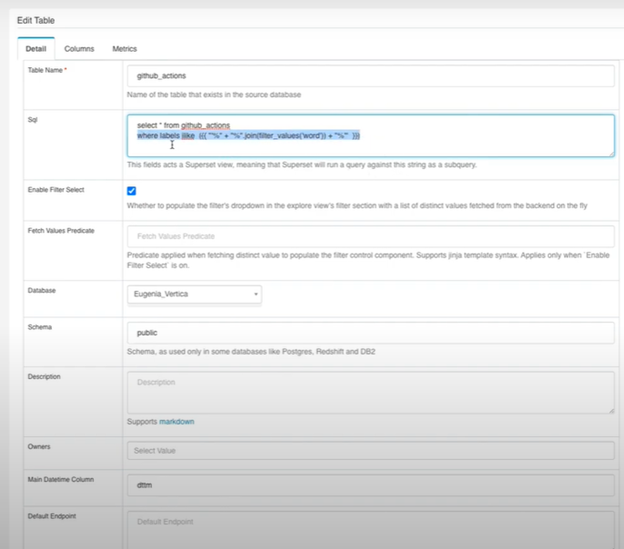
5�����、官方參考文檔:
https://superset.apache.org/docs/installation/sql-templating
官方?jīng)]有那么詳細,但是里面有一些我這里可能也沒有消化吸收掉�,可以參考看下
總之,通過上面的自定義參數(shù)方法���,和jinja表達式在sql中的應(yīng)用�����,可以實現(xiàn)動態(tài)查詢�����,解決一些無法通過頁面直接交互查詢結(jié)果顯示的內(nèi)容
另外如果你有其他應(yīng)用或者自定義上的思考�����,歡迎留言����,相互學習
到此這篇關(guān)于Superset實現(xiàn)動態(tài)SQL查詢的文章就介紹到這了,更多相關(guān)Superset動態(tài)SQL查詢內(nèi)容請搜索腳本之家以前的文章或繼續(xù)瀏覽下面的相關(guān)文章希望大家以后多多支持腳本之家���!
您可能感興趣的文章:- 使用 Apache Superset 可視化 ClickHouse 數(shù)據(jù)的兩種方法
- superset在linux和windows下的安裝和部署詳細教程
- JPA多條件復(fù)雜SQL動態(tài)分頁查詢功能
- Mybatis模糊查詢和動態(tài)sql語句的用法
- Java的MyBatis框架中對數(shù)據(jù)庫進行動態(tài)SQL查詢的教程
- MyBatis實踐之動態(tài)SQL及關(guān)聯(lián)查詢