前言
PyTorch作為一款深度學習框架�����,已經(jīng)幫助我們實現(xiàn)了很多很多的功能了���,包括數(shù)據(jù)的讀取和轉換了,那么這一章節(jié)就介紹一下PyTorch內(nèi)置的數(shù)據(jù)讀取模塊吧
模塊介紹
- pandas 用于方便操作含有字符串的表文件���,如csv
- zipfile python內(nèi)置的文件解壓包
- cv2 用于圖片處理的模塊,讀入的圖片模塊為BGR,N H W C
- torchvision.transforms 用于圖片的操作庫�����,比如隨機裁剪�、縮放、模糊等等��,可用于數(shù)據(jù)的增廣��,但也不僅限于內(nèi)置的圖片操作�,也可以自行進行圖片數(shù)據(jù)的操作,這章也會講解
- torch.utils.data.Dataset torch內(nèi)置的對象類型
- torch.utils.data.DataLoader 和Dataset配合使用可以實現(xiàn)數(shù)據(jù)的加速讀取和隨機讀取等等功能
import zipfile # 解壓
import pandas as pd # 操作數(shù)據(jù)
import os # 操作文件或文件夾
import cv2 # 圖像操作庫
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt # 圖像展示庫
from torch.utils.data import Dataset # PyTorch內(nèi)置對象
from torchvision import transforms # 圖像增廣轉換庫 PyTorch內(nèi)置
import torch
初步讀取數(shù)據(jù)
數(shù)據(jù)下載到此處
我們先初步編寫一個腳本來實現(xiàn)圖片的展示
# 解壓文件到指定目錄
def unzip_file(root_path, filename):
full_path = os.path.join(root_path, filename)
file = zipfile.ZipFile(full_path)
file.extractall(root_path)
unzip_file(root_path, zip_filename)
# 讀入csv文件
face_landmarks = pd.read_csv(os.path.join(extract_path, csv_filename))
# pandas讀出的數(shù)據(jù)如想要操作索引 使用iloc
image_name = face_landmarks.iloc[:,0]
landmarks = face_landmarks.iloc[:,1:]
# 展示
def show_face(extract_path, image_file, face_landmark):
plt.imshow(plt.imread(os.path.join(extract_path, image_file)), cmap='gray')
point_x = face_landmark.to_numpy()[0::2]
point_y = face_landmark.to_numpy()[1::2]
plt.scatter(point_x, point_y, c='r', s=6)
show_face(extract_path, image_name.iloc[1], landmarks.iloc[1])

使用內(nèi)置庫來實現(xiàn)
實現(xiàn)MyDataset
使用內(nèi)置庫是我們的代碼更加的規(guī)范�����,并且可讀性也大大增加
繼承Dataset,需要我們實現(xiàn)的有兩個地方:
- 實現(xiàn)
__len__返回數(shù)據(jù)的長度����,實例化調(diào)用len()時返回
__getitem__給定數(shù)據(jù)的索引返回對應索引的數(shù)據(jù)如:a[0]transform 數(shù)據(jù)的額外操作時調(diào)用
class FaceDataset(Dataset):
def __init__(self, extract_path, csv_filename, transform=None):
super(FaceDataset, self).__init__()
self.extract_path = extract_path
self.csv_filename = csv_filename
self.transform = transform
self.face_landmarks = pd.read_csv(os.path.join(extract_path, csv_filename))
def __len__(self):
return len(self.face_landmarks)
def __getitem__(self, idx):
image_name = self.face_landmarks.iloc[idx,0]
landmarks = self.face_landmarks.iloc[idx,1:].astype('float32')
point_x = landmarks.to_numpy()[0::2]
point_y = landmarks.to_numpy()[1::2]
image = plt.imread(os.path.join(self.extract_path, image_name))
sample = {'image':image, 'point_x':point_x, 'point_y':point_y}
if self.transform is not None:
sample = self.transform(sample)
return sample
測試功能是否正常
face_dataset = FaceDataset(extract_path, csv_filename)
sample = face_dataset[0]
plt.imshow(sample['image'], cmap='gray')
plt.scatter(sample['point_x'], sample['point_y'], c='r', s=2)
plt.title('face')
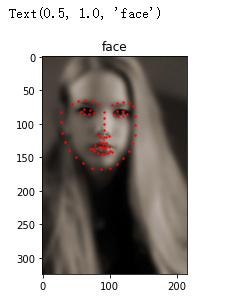
實現(xiàn)自己的數(shù)據(jù)處理模塊
內(nèi)置的在torchvision.transforms模塊下,由于我們的數(shù)據(jù)結構不能滿足內(nèi)置模塊的要求�����,我們就必須自己實現(xiàn)
圖片的縮放���,由于縮放后人臉的標注位置也應該發(fā)生對應的變化���,所以要自己實現(xiàn)對應的變化
class Rescale(object):
def __init__(self, out_size):
assert isinstance(out_size,tuple) or isinstance(out_size,int), 'out size isinstance int or tuple'
self.out_size = out_size
def __call__(self, sample):
image, point_x, point_y = sample['image'], sample['point_x'], sample['point_y']
new_h, new_w = self.out_size if isinstance(self.out_size,tuple) else (self.out_size, self.out_size)
new_image = cv2.resize(image,(new_w, new_h))
h, w = image.shape[0:2]
new_y = new_h / h * point_y
new_x = new_w / w * point_x
return {'image':new_image, 'point_x':new_x, 'point_y':new_y}
將數(shù)據(jù)轉換為torch認識的數(shù)據(jù)格式因此����,就必須轉換為tensor
注意: cv2和matplotlib讀出的圖片默認的shape為N H W C,而torch默認接受的是N C H W因此使用tanspose轉換維度�,torch轉換多維度使用permute
class ToTensor(object):
def __call__(self, sample):
image, point_x, point_y = sample['image'], sample['point_x'], sample['point_y']
new_image = image.transpose((2,0,1))
return {'image':torch.from_numpy(new_image), 'point_x':torch.from_numpy(point_x), 'point_y':torch.from_numpy(point_y)}
測試
transform = transforms.Compose([Rescale((1024, 512)), ToTensor()])
face_dataset = FaceDataset(extract_path, csv_filename, transform=transform)
sample = face_dataset[0]
plt.imshow(sample['image'].permute((1,2,0)), cmap='gray')
plt.scatter(sample['point_x'], sample['point_y'], c='r', s=2)
plt.title('face')
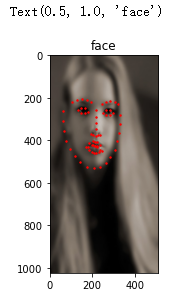
使用Torch內(nèi)置的loader加速讀取數(shù)據(jù)
data_loader = DataLoader(face_dataset, batch_size=4, shuffle=True, num_workers=0)
for i in data_loader:
print(i['image'].shape)
break
torch.Size([4, 3, 1024, 512])
注意: windows環(huán)境盡量不使用num_workers會發(fā)生報錯
總結
這節(jié)使用內(nèi)置的數(shù)據(jù)讀取模塊,幫助我們規(guī)范代碼�,也幫助我們簡化代碼,加速讀取數(shù)據(jù)也可以加速訓練�����,數(shù)據(jù)的增廣可以大大的增加我們的訓練精度�,所以本節(jié)也是訓練中比較重要環(huán)節(jié)
到此這篇關于PyTorch數(shù)據(jù)讀取的實現(xiàn)示例的文章就介紹到這了,更多相關PyTorch數(shù)據(jù)讀取內(nèi)容請搜索腳本之家以前的文章或繼續(xù)瀏覽下面的相關文章希望大家以后多多支持腳本之家!
您可能感興趣的文章:- 關于PyTorch源碼解讀之torchvision.models
- pytorch實現(xiàn)ResNet結構的實例代碼
- PyTorch實現(xiàn)ResNet50�、ResNet101和ResNet152示例
- 關于ResNeXt網(wǎng)絡的pytorch實現(xiàn)
- pytorch教程resnet.py的實現(xiàn)文件源碼分析