看到這個題目你可能覺得這是什么鬼�? 其實我想說的是這種,看下面的錄制:
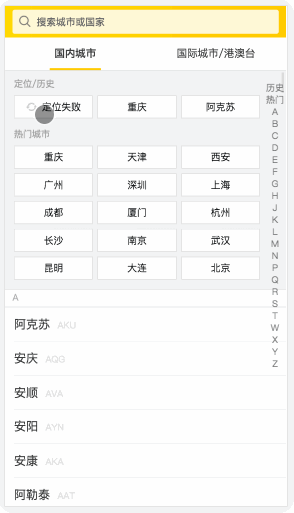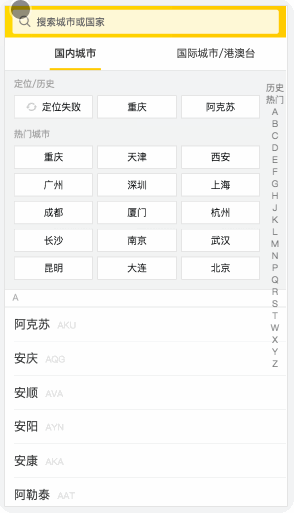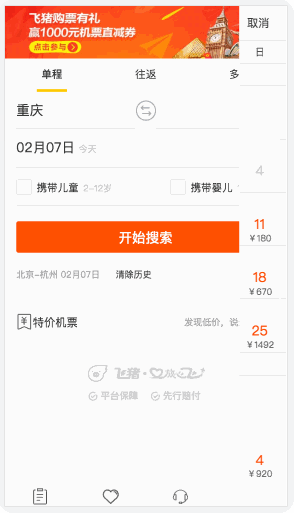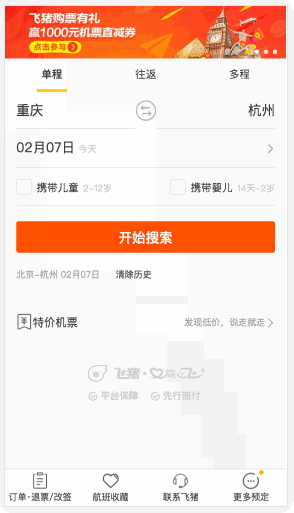
這種交互在H5頁面中比比皆是��,點擊城市->彈出城市選擇浮層->按返回按鈕關閉浮層����。
這些操作都是不要點擊左上角/右上角的關閉按鈕就可以進行的,飛豬的H5是前進出現(xiàn)彈層���,返回時彈層關閉,其他家都不行(去哪兒網(wǎng)H5飛機票����,美團H5酒店)。
為什么要這么設計?
因為H5是在手機上操作的�����,手機上的手指可操作區(qū)域的覆蓋范圍很小���,更別說左上角/右上角這些死角(取消/關閉)區(qū)域了����。你肯定聽過這個操作:輕觸返回���。這個在用戶操作的時候非常方便友好����,選擇完城市后�����,不需要點擊取消���,直接在大拇指可以操作的地方點擊返回就關閉了彈層。
如何實現(xiàn)
既然有這種非常好的需求����,那作為開發(fā)肯定就會想法設法的實現(xiàn)這個功能了。 你甚至都不用google�,你就應該會想到類似的history.back(),history.go()這些方法了����。 然而想到這些依舊沒用,理論上 瀏覽器/webview 的返回/前進的是要重新加載頁面的����,因為URL發(fā)生了變化��。 如果你真的知道單頁面應用(SPA),或者使用React/Vue你就應該知道有個東西叫:路由�����。 這些通過改變hash且無法刷新的url變化是HTML5時加入的history功能
the-history-interface
interface History {
readonly attribute unsigned long length;
attribute ScrollRestoration scrollRestoration;
readonly attribute any state;
void go(optional long delta = 0);
void back();
void forward();
void pushState(any data, DOMString title, optional DOMString? url = null);
void replaceState(any data, DOMString title, optional DOMString? url = null);
};
- pushState
- replaceState
還有一個事件
- onpopstate
pushState���,replaceState 用來改變histroy堆棧順序,onpopstate 在返回��,前進的時候觸發(fā)
vue-router中的實現(xiàn)也是如此(第1694行)
具體實現(xiàn)
既然說了這么多�����,那我們來看下怎么實現(xiàn)這種功能���。
來看下 pushState 和 replaceState 的兼容性
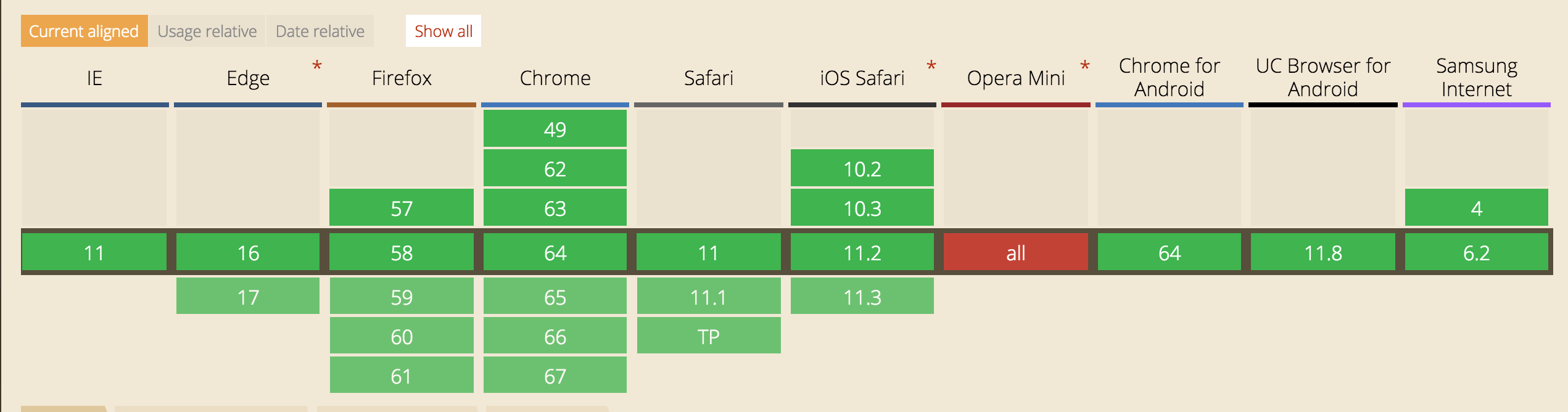
全綠����,用起來放心多了�����。
思路:
- 點擊彈層時 pushState 添加 hash
- "輕觸返回"的時候觸發(fā) onpopstate 事件時候隱藏彈層并修改 hash
<button onclick="city()">
城市
</button><br>
<button onclick="calendar()">
日歷
</button><br>
<button onclick="description()">
說明
</button>
<div id="city" class="com" style="display: none;">
模擬城市彈框層
</div>
<div id="calendar" class="com" style="display: none;">
模擬日歷彈框層
</div>
<div id="description" class="com" style="display: none;">
模擬說明彈框層
</div>
button {
border: #0000;
background-color: #f90;
}
.com {
position: absolute ;
top: 0;
bottom: 0;
left: 0;
right: 0;
background-color: #888589;
}
var cityNode = document.getElementById('city');
var calendarNode = document.getElementById('calendar');
var descriptionNode = document.getElementById('description');
function city() {
cityNode.style.display = 'block';
window.history.pushState({'id':'city'},'','#city')
}
function calendar() {
calendarNode.style.display = 'block';
window.history.pushState({'id':'calendar'},'','#calendar')
}
function description() {
descriptionNode.style.display = 'block';
window.history.pushState({'id':'description'},'','#description')
}
window.addEventListener('popstate', function(e){
// alert('state:' + e.state + ', historyLength:' + history.length);
if (e.state && e.state.id === 'city') {
history.replaceState('','','#');
cityNode.style.display = 'block';
} else if (e.state && e.state.id === 'calendar') {
history.replaceState('','','#');
calendarNode.style.display = 'block';
} else if (e.state && e.state.id === 'description') {
history.replaceState('','','#');
descriptionNode.style.display = 'block';
} else {
cityNode.style.display = 'none';
calendarNode.style.display = 'none';
descriptionNode.style.display = 'none';
}
})
主要看 JS 代碼�,監(jiān)聽頁面的前進和后退事件來控制history�����。

源碼在此
以上就是本文的全部內容�����,希望對大家的學習有所幫助�����,也希望大家多多支持腳本之家。