目錄
- Python深搜版:
- Python 廣搜版
- lua版:
Python深搜版:
核心在于帶隨機的深搜(見代碼第23到27行,其實也可以用22行代替這幾行代碼�,你可以試著把第24行的數(shù)字4改大或者改小,即調(diào)整隨機程度)
import os
import random
from queue import Queue
import numpy
import colorama
from colorama import Fore, Back, Style
import sys
from bmpEditor import bmp
colorama.init()
# numpy.random.seed(1)
_xy = [0,2,0,-2,0]
size = 31
sys.setrecursionlimit(100000000)
road = set()
def dfs(curr_pos):
road.add(curr_pos)
# for i in numpy.random.permutation(4):
p = [0,1,2,3]
for i in range(4):
l = random.randint(0,3)
r = random.randint(0,3)
p[l], p[r] = p[r], p[l]
for i in p:
next_pos = (curr_pos[0] + _xy[i], curr_pos[1] + _xy[i+1])
if (0=next_pos[0]size and
0=next_pos[1]size and
next_pos not in road ):
road.add(((curr_pos[0] + next_pos[0])/2, (curr_pos[1] + next_pos[1])/2))
dfs(next_pos)
dfs((0,0))
q = Queue()
q.put((0,0))
ans_road = set()
def dfs_getans(curr_pos):
# print(curr_pos)
ans_road.add(curr_pos)
if (size-1, size-1) in ans_road:
return
for i in range(4):
next_pos = (curr_pos[0] + _xy[i]//2, curr_pos[1] + _xy[i+1]//2)
if (0=next_pos[0]size and
0=next_pos[1]size and
next_pos in road and
next_pos not in ans_road and
(size-1, size-1) not in ans_road):
dfs_getans(next_pos)
if (size-1, size-1) not in ans_road:
ans_road.remove(curr_pos)
dfs_getans((0,0))
for i in range(size):
for j in range(size):
print((Back.WHITE + ' ') if (i,j) in road else (Back.BLACK + ' '), end=' ')
print()
wall_width = 2
cell_size = 6
image = bmp((size+3)*cell_size-wall_width, (size+3)*cell_size-wall_width, 0x000000)
for i in range(size+3):
for j in range(size+3):
if (i-1, j-1) in road:
image.paint_rect(i*cell_size, j*cell_size, cell_size*2-wall_width, cell_size*2-wall_width, 0xffffff)
file_name = "%dmaze.bmp"%size
image.save_image(file_name)
os.system(file_name)
for p in ans_road:
# image.paint_rect(p[0]+1, p[1]+1)
image.paint_rect((
p[0]+1)*cell_size + (cell_size - wall_width)//2,
(p[1]+1)*cell_size + (cell_size - wall_width)//2,
cell_size, cell_size,
0xff0000
)
file_name = "%dans.bmp"%size
image.save_image(file_name)
os.system(file_name)
效果
3131:

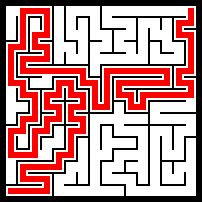
8181:
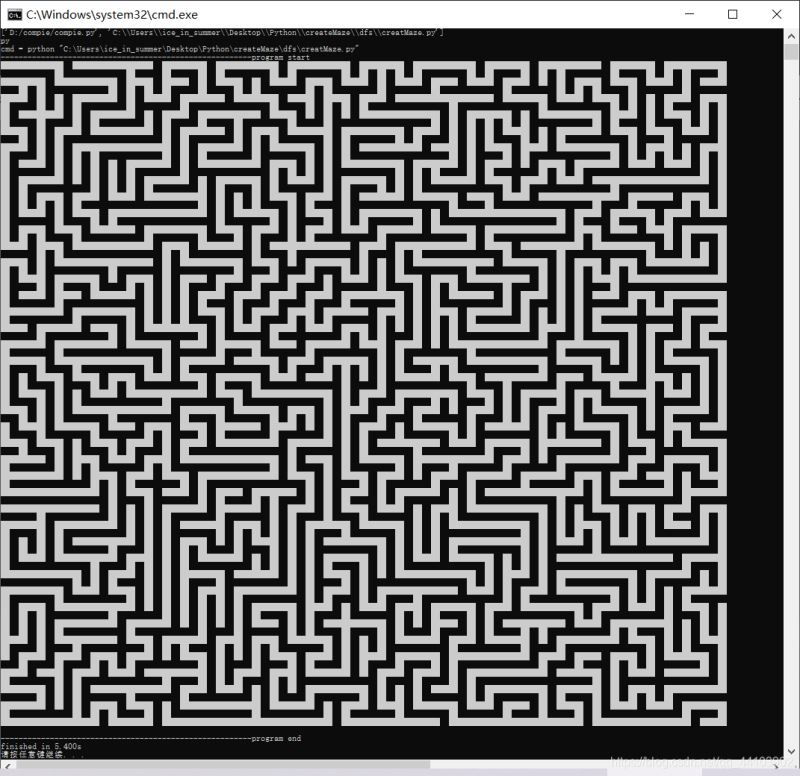
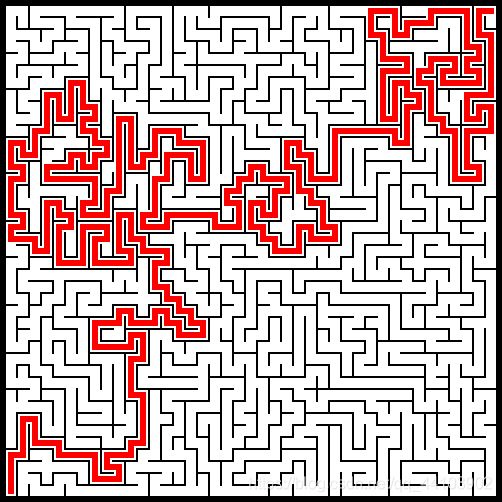
坐標系有翻轉(zhuǎn)���,控制臺中的左上角對應(yīng)圖片中的左下角
其中bmpEditor不是官方庫�,代碼地址(文件名為bmpEditor.py�����,和這以上代碼放同一個路徑下即可)
Python 廣搜版
在隊列的基礎(chǔ)上把隊列中的元素順序打亂(第24行)
import os
import random
from queue import Queue
import numpy
import colorama
from colorama import Fore, Back, Style
import sys
import random
from bmpEditor import bmp
colorama.init()
numpy.random.seed(1)
_xy = [0,2,0,-2,0]
size = 59
sys.setrecursionlimit(size*size//4+size)
q = []
q.append((0,0))
road = set()
road.add((0,0))
while len(q) != 0:
random.shuffle(q)
curr_pos = q.pop()
# print(curr_pos)
for i in range(4):
next_pos = (curr_pos[0] + _xy[i], curr_pos[1] + _xy[i+1])
if ( 0=next_pos[0]size and
0=next_pos[1]size and
next_pos not in road ):
road.add( ((curr_pos[0] + next_pos[0])//2, (curr_pos[1] + next_pos[1])//2) )
q.append(next_pos)
road.add(next_pos)
ans_road = set()
def dfs_getans(curr_pos):
ans_road.add(curr_pos)
if (size-1, size-1) in ans_road:
return
for i in range(4):
next_pos = (curr_pos[0] + _xy[i]//2, curr_pos[1] + _xy[i+1]//2)
if ( 0=next_pos[0]size and
0=next_pos[1]size and
next_pos in road and
next_pos not in ans_road and
(size-1, size-1) not in ans_road):
dfs_getans(next_pos)
if (size-1, size-1) not in ans_road:
ans_road.remove(curr_pos)
dfs_getans((0,0))
print(len(ans_road))
for i in range(0, size):
for j in range(0, size):
print((Back.WHITE + ' ') if (i,j) in road else (Back.BLACK + ' '), end=' ')
print()
wall_width = 1
cell_size = 5
image = bmp((size+3)*cell_size-wall_width, (size+3)*cell_size-wall_width, 0x000000)
for i in range(size+3):
for j in range(size+3):
if (i-1, j-1) in road:
image.paint_rect(i*cell_size, j*cell_size, cell_size*2-wall_width, cell_size*2-wall_width, 0xffffff)
file_name = "%dmaze.bmp"%size
image.save_image(file_name)
os.system(file_name)
for p in ans_road:
# image.paint_rect(p[0]+1, p[1]+1)
image.paint_rect((
p[0]+1)*cell_size + (cell_size - wall_width)//2,
(p[1]+1)*cell_size + (cell_size - wall_width)//2,
cell_size, cell_size,
0xff0000
)
file_name = "%dans.bmp"%size
image.save_image(file_name)
os.system(file_name)
效果:

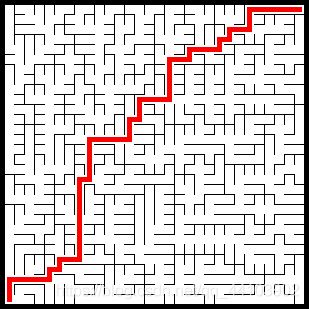
相比深度優(yōu)先的�����,這種迷宮會更加“直”一些
lua版:
大體上是深搜�����,加了一定的隨機性使得搜索過程中有一定概率暫時放棄當前路徑。見表stop_points���,(第7行��、第74行及其后面的repeat循環(huán))
local _xy = {0,2,0,-2,0}
local size = 41
local base = size+1
local road = {}
stop_points = {}
function dfs(curr_x, curr_y)
road[curr_x*base+curr_y] = true
if math.random(1,10) = 3 then
stop_points[curr_x*base+curr_y] = true
return
end
-- os.execute("cls")
-- print_map()
local permutation = {1,2,3,4}
for i=1, 4 do
local l = math.random(1,4)
local r = math.random(1,4)
permutation[l], permutation[r] = permutation[r], permutation[l]
end
for i=1, 4 do
local next_x = curr_x+_xy[permutation[i]]
local next_y = curr_y+_xy[permutation[i]+1]
if next_x>=1 and next_x=size and
next_y>=1 and next_y=size and
road[next_x*base+next_y] == nil then
local mid_x = math.floor((curr_x+next_x)/2)
local mid_y = math.floor((curr_y+next_y)/2)
road[mid_x*base+mid_y] = true
dfs(next_x, next_y)
end
end
end
local ans_geted = false
local parent = {}
function get_ans(curr_x, curr_y)
-- print(curr_x, curr_y)
for i=1, 4 do
next_x = (curr_x + math.floor(_xy[i])/2 )
next_y = (curr_y + math.floor(_xy[i+1])/2 )
-- print(next_x, next_y)
if next_x >= 1 and next_x = size and
next_y >= 1 and next_y = size and
road[next_x*base+next_y] and
parent[next_x*base+next_y]==nil
then
parent[next_x*base+next_y] = curr_x*base+curr_y
get_ans(next_x, next_y)
end
end
end
local ans_road = {}
function print_map()
for i=0, size+1 do
local line = ""
for j=0, size+1 do
if ans_road [i*base+j] then
line = line..".."
elseif road[i*base+j]==true then
line = line.." "
else
line = line.."HH"
end
end
print(line)
end
end
stop_points[1*base+1] = true
-- create maze
repeat
local has_point = false
for v,_ in pairs(stop_points) do
has_point = true
stop_points[v] = nil
dfs(math.floor(v/base), v%base)
break
end
-- print(has_point)
until not has_point
get_ans(1,1)
parent[1*base+1] = nil
print("")
-- for k,v in pairs(parent) do
-- print(string.format("[%d,%d]->[%d,%d]", math.floor(k/base), k%base, math.floor(v/base), v%base))
-- end
print("")
local x = size
local y = size
repeat
-- print(x,y)
ans_road[x*base+y] = true
local v = parent[x*base+y]
x = math.floor(v/base)
y = v%base
until --[[(x==1 and y== 1)]] not parent[x*base+y]
ans_road[1*base+1] = true
print_map()
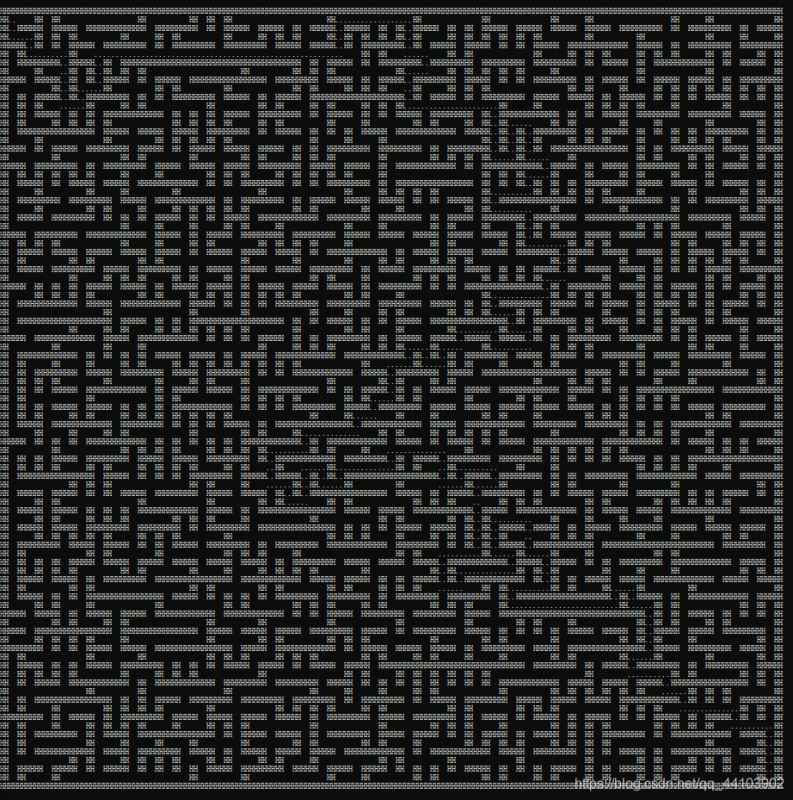
效果:
4141:
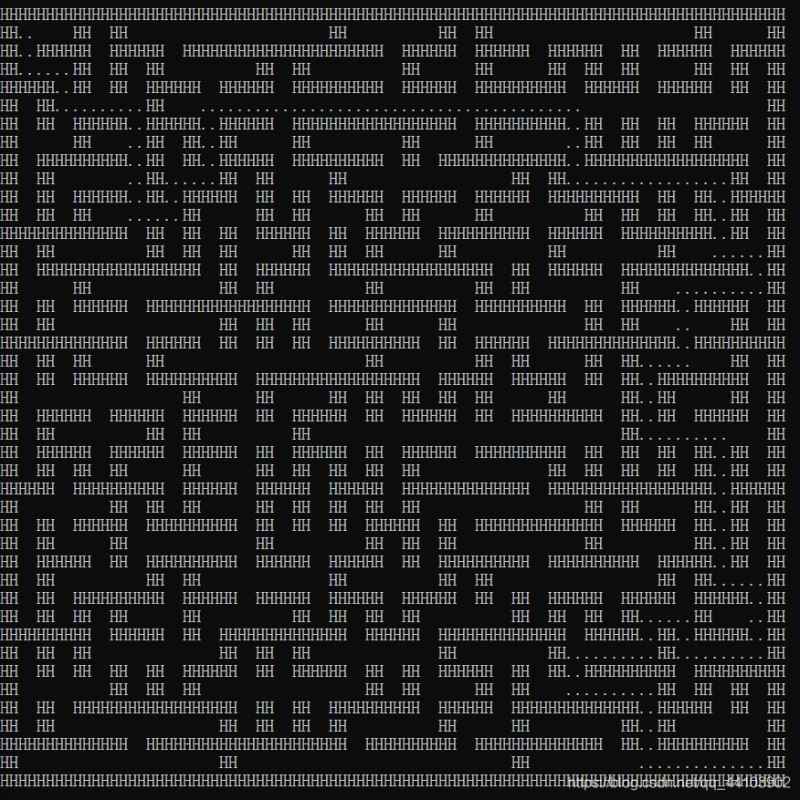
8989
到此這篇關(guān)于Python實現(xiàn)隨機生成迷宮并自動尋路的文章就介紹到這了,更多相關(guān)Python生成迷宮并自動尋路內(nèi)容請搜索腳本之家以前的文章或繼續(xù)瀏覽下面的相關(guān)文章希望大家以后多多支持腳本之家���!
您可能感興趣的文章:- Javascript結(jié)合Vue實現(xiàn)對任意迷宮圖片的自動尋路
- C++ DFS算法實現(xiàn)走迷宮自動尋路
- PHP樹的深度編歷生成迷宮及A*自動尋路算法實例分析